It is imperative to make available to the citizens of Mehsana district, the
basic needs such as education, health, drinking water, employment and sanitation
as when most of the countries of the world are making efforts for the achievements
of better human development index.
• Health and nutrition.
The present health policy aims at providing health services to the masses
on the basis of qualitative referral system and infrastructural coordination. In
Mehsana district, at present 11 community health centres, 49 Primary health
centres, 288 sub centres and 6 dispensaries are functioning. Moreover, NGOs
and private practitioners are carrying out health-related works in the district. Despite
this, serious health-related social problems have emerged. The ratio of HIV/
AIDS, Anaemia, TB, child/mother mortality ratio has reached an alarming stage.
HIV/AIDS a burning problem.
 As per sentinel surveillance
in Mehsana
district, the HIV ratio is between 1.0% to 1.5%.
Evidently, the HIV has spread into general population.
The reason is single male out migration
in diamond industry, couriers, and looms, particularly
in Surat city or elsewhere. The fall in
female child ratio is also a reason. Hence, HIV is spreading out in the district
causing various social economic and educational problems in the district. Positive
efforts have been made to combat these issues in the district and steps have
been taken to render services for condom distribution, STI (Sexually Transmitted
Infection) and counselling. Moreover, venereal diseases control programmes;
blood safety programmes etc. have been implemented. The role of Young Citizen
has remained very important.
As per sentinel surveillance
in Mehsana
district, the HIV ratio is between 1.0% to 1.5%.
Evidently, the HIV has spread into general population.
The reason is single male out migration
in diamond industry, couriers, and looms, particularly
in Surat city or elsewhere. The fall in
female child ratio is also a reason. Hence, HIV is spreading out in the district
causing various social economic and educational problems in the district. Positive
efforts have been made to combat these issues in the district and steps have
been taken to render services for condom distribution, STI (Sexually Transmitted
Infection) and counselling. Moreover, venereal diseases control programmes;
blood safety programmes etc. have been implemented. The role of Young Citizen
has remained very important.
Supplementary nutrition and Anaemia.
The NHFS - 3 report reveals that 42% children of the State have low height
as per age, whereas 17% children are underweight as per age. Government and
NGOs have taken steps to increase the level of nutrition in mothers and children.
The malnutrition among women, children and adolescent girls in Mehsana district
has reached a very serious level.
The Status of important health measures in Mehsana.
Health services play a very vital role and hence they are provided through
the network of various programmes of child development, safe motherhood,
family planning and extension of health services to the active age group of children
in the area. However, in Mehsana district a total of 46156-birth registration were
reported in the year 2010. Against this, the number of death registered were
12376. Infant mortality (0 to 2 months) registration is 170 and 216 stillbirth were
registered. In view of important health indicators, the leading Talukas of Mehsana
district stand as under:
Important events registered and vital data available for town as per
population.
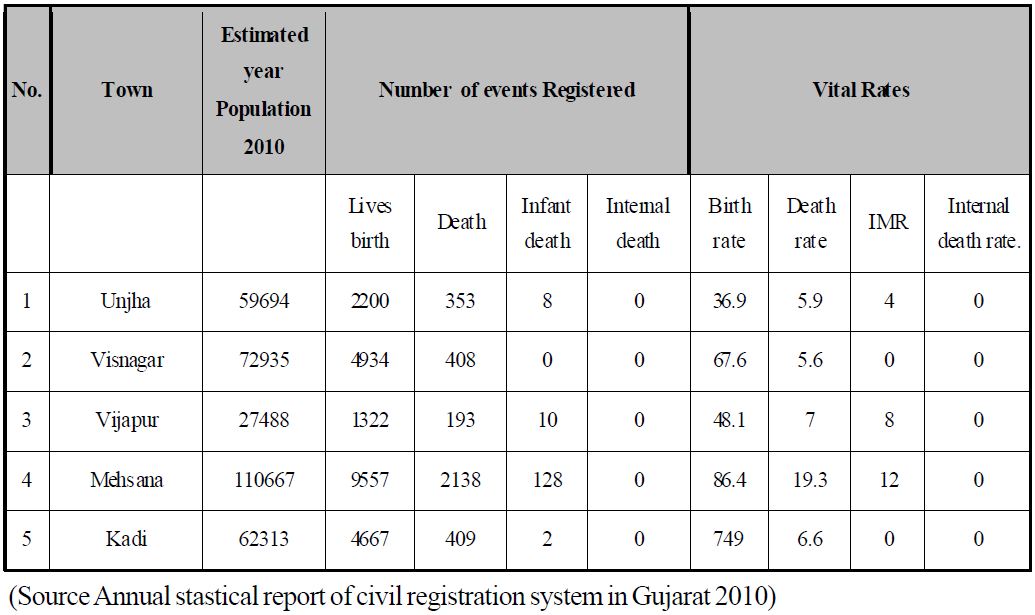
Above table shows that as per CRS 2010, in Mehsana district the birth ratio was
21.1 in rural areas and 62.0 in urban area. The mortality ratio in rural area was 5.7
and that in urban area was 8.6. IMR is two in rural area and five in urban area. Out
of total population of Mehsana district 76.65% is rural and 25.35% urban. Though
the medical facilities both Government and private, are more in urban areas as
compared to that in rural areas, the picture of general health remains somewhat
better in rural areas. The urban sector, therefore requires much emphasis on this
aspect.
Education
 The most
remarkable finding is that the
primary education has constantly remained the
source to upgrade the life standard of any
nation. It has a positive impact on all sectors
such as health, employment, child development
and women empowerment. The investment made
in this sector is capable of rewarding a lot. Primary education is the base of
pyramid of education. The literacy level in Mehsana district, in comparison to
other Indian States is slightly disappointing. This level requires to be upgraded in
the district with the help of civil society, private sector and the government on
research and analysis basis.
The most
remarkable finding is that the
primary education has constantly remained the
source to upgrade the life standard of any
nation. It has a positive impact on all sectors
such as health, employment, child development
and women empowerment. The investment made
in this sector is capable of rewarding a lot. Primary education is the base of
pyramid of education. The literacy level in Mehsana district, in comparison to
other Indian States is slightly disappointing. This level requires to be upgraded in
the district with the help of civil society, private sector and the government on
research and analysis basis.
Environment
The environmental protection in the State is based on (1) environment has
a sound linkage with human development; (2) environment in Gujarat has less
and adverse effect which need prime attention. In Gujarat, more than half of the
population is in primary sector and depends mainly on natural resources for
employment and economic needs.
Water resources.
The decrease and fall of water resources is mainly due to water supply to
the industries. A big gap is in demand and supply of water in the State. Unless the
water resources are strengthened and the use of water is streamlined, there is no hope to overcome
the serious water crisis in the State.
The percentage of problematic talukas for ground water in the Gujarat State.
Mehsana, Banaskantha and Gandhinagar districts are in the category of
higher water consumption. The State is facing serious scarcity of drinking water.
The Saurashtra, Kutch and North Gujarat are highly affected and that adversely
affects the general hygienic condition of the people. The Mehsana district of North
Gujarat has a serious crisis both on quality and quantity of water.
As per the survey, of 1646 villages, 522 villages are having the highest
fluoride ratio, whereas 23 villages are having the highest nitrate ratio. Schemes of
water purification require to be formulated in these areas.
• Forest Resources:
The conservation of forests assumes a great significance especially in tribal
dominated areas as the main source of their livelihood depends on the forest
produce and therefore it is essential to support their economic activities in the area. The
reduction in forest cover adversely affect the people dependent on
forest produce and also human development naturally.
The latest forest survey revealed that 6.6% area of Gujarat is under forest.
Actually, the registered forest area of total geographical area is 10%. The dense
forest area of the State is about 32%. The main forest areas of the State are Central
Saurashtra (Gir forest) and dense forest around Gulf of Kutch. The illicit cutting
of trees, theft of teak and timber wood, encroachment etc. are the main factors
responsible for the reduction of forests. This creates a negative effect on the life
and livelihood of tribals resulting in their large scale migration.
• Land Resources
Forest is a basic unit of any Government. It has three fold actions
(1) Land based economic activities.
(2) Land and climate oriented scientific activities.
(3) Non-land based economic activities.
It is worthwhile to allot land on a stable and proper system for various usages.
Generally, desert is created due to improper arrangement of natural resources
and their extensive utilization. It has been noticed that deserts in the northern part
of the State have increased gradually, in the Kutch, Banaskantha and North
Saurashtra. The reports on the issue states that this process is alarming and
requires to be prevented urgently.
Gujarat has arid zones in 8 districts. Due to loss of vegetation, lot of area
is open to erosion. Water and wind degrade the texture of the land. The excessive
use of irrigation has caused waterlogging and salinity which adversely affects the
cropping pattern at large. The abundant use of irrigation and that of natural
resources has caused abolition of forest. The misuse of natural resources has
created deserts in the various parts of North Gujarat.
• Draught in Gujarat.
Draught has an adverse effect on human welfare due to scanty rainfall.
Scarcity of water affects yielding of crops and amount to loss of agricultural
products. The intensity of draught affects human development, health, education,
etc in a long run, it affects the eco-system and Environment, too.
The recurrence of drought adversely affects the water resources, forest
resources, livestock, fisheries, etc. and thereby affects the economic development
of the area. In Gujarat out of 184 Talukas, 52 are under the drought prone
area program, and 47 Talukas are under desert development program. The ratio
of drought is very high in Gujarat and therefore scarcity and relief works are
needed to be taken up. Due to drought situation, there is a serious scarcity of
drinking water in the State, which is also due to shortage of water resources. This
situation also creates a serious impact on economy of the people. They have to
face various hardships to keep their body and soul together. The per capita
income falls year-by-year causing migration, mortgaging of their assets, etc. ultimately
resulting in low living standards of the people.
• Rescue, relief and rehabilitation.
Droughts being a natural calamity the relief works are undertaken by the
Revenue Department. The relief works include work for employment, water
supply, fodder, and cattle camps etc. The relief works aim at (1) control and
supervision on relief work, (2) start relief work and provide drinking water and
fodder for cattles, allow subsidy to farmers and distribute cash dole etc. (3)
better implementation of relief works to provide fund, means and tools etc.
• Pollution, air, water and land:
The various possibilities of pollution that affect the environment of Gujarat are:
1. The land, water and vegetation are chiefly affected by the industrialization, solid waste
sewerage etc.
2. Excavation of minerals from mines creates pollution due to dust, blast and
explosives.
3. Use of pesticides and fertilizers in agriculture adversely affect the texture
of the land. The exhausted water resources may also pollute land, water
and vegetation.
4. The carbon monoxide, dioxide emission from vehicles etc pollute the
atmosphere.
5. The human excreta and improper disposal of bio-Medical waste from hos
pitals, etc pollute air, land and vegetation at large.
6. The internal pollutions in factories and residences go up.
• Concluding observations:
The environment resources in Gujarat have shown a remarkable decrease
in the present decades. of course, no state can prevent the loss of natural resources
in its process of economic growth. pollution also travels with economic
growth. However, it is imperative to make available to the people, the minimum
needs of life such as pure drinking water, fresh air and clean atmosphere. This
needs to be achieved.
Lot many NGOs have revealed that human development and management
of natural resources go hand in hand. As the programmes are widely taken up
with a change in policy, at large, it also requires strong commitment.
• Employment and training:
The overall change in world economy have also made some change in the
structure of employment recently. People are now more inclined towards general
industry and service industry instead of farming. The percentage of agricultural
sector has decreased in comparison to percentage of industrial sector, as
with reference to national Income.
• Gender Development:
Human development is a process of extension of opportunities and choice
for all, people and if women are deprived of this benefit, the whole process
becomes unjust and unfair. Women have no choice in social, political and economic
sector in the process of modern development, because the opportunities
for women in capacity building are limited and the conventional social, cultural,
political and economic atmosphere put a limit on their use of capacity. Society,
in general, does not however provide equal opportunities to the women. In the
last two decades, capacity of women has expanded but extension of opportunities
to them has remained less.
Government of India has adopted a policy of women empowerment in the year
2001. In India, particularly married women become victim of violence due to
demand of dowry, resulting into suicide or death. Right from childhood to old
age, women are always under a threat of violence. The girl child is killed in
embryo i.e. violence takes place even before birth. In the urban sector of development
in India, sex determination is rampant. The male vs. female ratio is
alarmingly low.
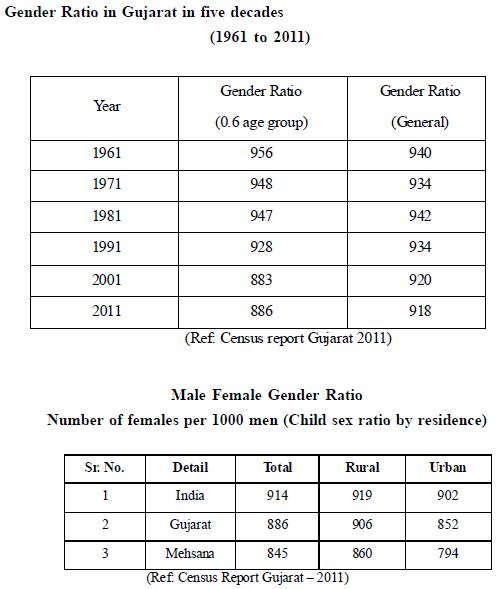
• Male - Female sex ratio - Mehsana district:
It is a common belief that if male child is born, it is full stop and if it is
female child, it is semi colon. As per census of 2001, the male female ratio is
1000:918. The lowest female ratio i.e. 760 seen in Mehsana district, is the lowest
in India. The falling gender ratio has created serious social problems giving rise to
HIV ratio. Moreover many other social problems also make the situation
complex.